Strategy Execution Anchored in Business Capabilities

Strategy execution is a vital process for business organizations since it underpins the application and adoption of strategies. Executing a strategy is the most important management challenge organizations face in the 21st century. Over 80% of organizations fail to execute their strategies effectively (Sull et al., 2015). In most cases, failure to execute a strategy is caused by poor execution, not due to a poor strategy. This is because most organizations lack the appropriate framework to execute their strategies, thus leading to failure.
Strategy execution is a contested subject in modem management. The significance of strategy execution lies in most CEOs’ perspectives, who consider it their major challenge. The operations of organizations revolve around strategy, but formulation and planning are easier than execution. Over 60% of strategies are not executed effectively, indicating the complexity of strategy execution in modern organizations (Barrows, 2019). The enterprise transformation process framework developed by Agile Dynamics offers logical and pragmatic rationale for effective strategy execution.
Enterprise Transformation Process Framework
The enterprise transformation process framework is iterative model with a feedback loop for creating clarity versus confusion in strategy execution based on differentiating business capabilities derived out of the strategy. It involves reflecting on all aspects of the organization, from its identity and culture over to value streams and unique business capabilities down to its services, products, and inflight projects. The enterprise transformation process framework helps companies embrace change initiatives, creating an environment that nurtures adapting to internal and external factors. In addition, it creates a transformation roadmap built around more than one future due to embedded business scenarios that account for critical variables from internal and external perspectives.
Five Stages Required for the Business Transformation
The enterprise transformation process framework entails five stages: Interpreting Strategy, Initiation, Definition, Adoption and Transition, and Performance Management.
Each process stage defines a vital set of interrelated tasks and activities in strategy execution that demystifies the process by creating clarity (Kotnour, 2011). The role of each stage leads to the overall success and effectiveness of strategy execution.
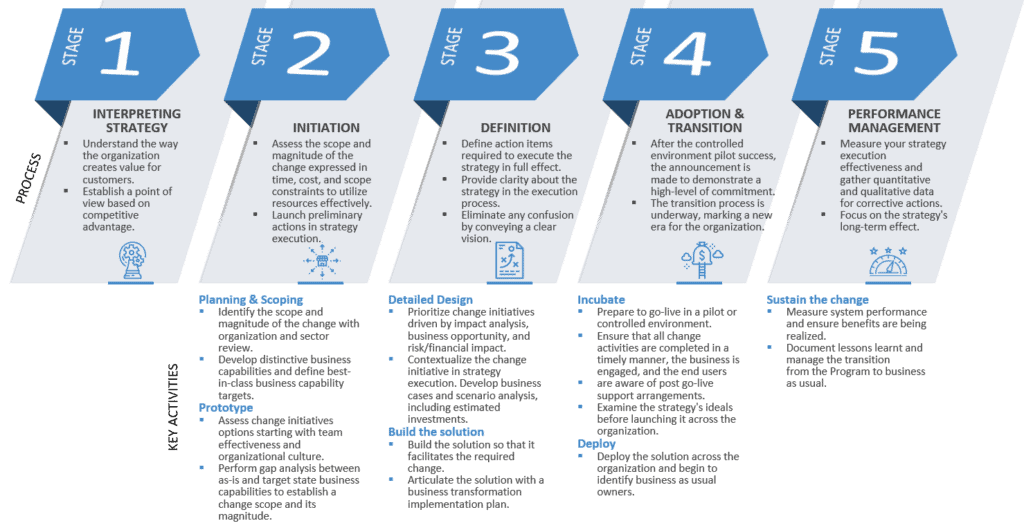
Stage 1: Interpreting Strategy involves understanding how organizations generate value for consumers and establishing a view based on competitive advantage. The strategy-to-execution procedure offers an organized tactic for managing, elucidating, implementing, and communicating.
Both internal and external analysis is required for a comprehensive organization and sector review. The objective is to certify that the organization creates valuable competencies and provides outlays that enhance value (Scott, 2016). Through interpretation, the strategy is contextualized in terms of the value generated while adhering to environmental, social and governance (ESG) priorities and at the same time providing targeted levels of shareholder returns in line with employees, clients, customers, and society expectations.
Stage 2: Initiation is about launching preliminary actions in strategy execution, which marks the beginning of a proactive transformation process. During Initiation, the scope and magnitude of the change are identified. Strategy execution starts through various practical processes aimed at fulfilling the strategy. Strategy execution as a process is a systematic way or discipline of exposing actuality by performing it (Barrows, 2019). The bedrock of the transformative change is based on distinctive business capabilities and defined best-in-class business capability targets aligned to value streams.
This will bring clarity and focus on the differentiating business capabilities required to add value to a customer from the initial request through realization of value by the customer. Beside the hard elements Initiation stage involves assessment of the top team effectiveness and organizational culture. As two critical success factors team effectiveness and organizational culture are considered as the price of the movie tickets; without it there is no show! Therefore, organizations must create an execution strategy accounting for multiple business scenarios, invest in people, and facilitate specific operations to execute a strategy effectively.
Stage 3: Definition brings clarity about the strategy in the execution process must be provided. This serves to eradicate confusion by heralding a clear vision for the organization. The modern business environment is fast-paced, and organizations find it difficult to formulate their strategy (Cheng, 2015). In a perfect world, managers could formulate a lasting strategy by considering what the organization requires and then systematically executing it. However, additional efforts are required.
In the Definition phase of the enterprise transformation process, action items required to execute the strategy in full effect are clearly defined. The strategy is delineated from other aspects of the organization, enhancing its clarity. The solution is designed so it facilitates the change and then articulated through a business transformation implementation plan.
Stage 4: Adoption and Transition is a major stage in strategy execution. The strategy is integrated into the organization’s routine operations, thus building a transition from the old to the new (Scott, 2016). Since strategy execution introduces a new direction throughout the organization, its adoption marks a new era. A transition is necessary to facilitate the practical role of the strategy in transforming the organization.
Stage 5: Performance Management involves measuring the results of strategy execution and integrating the insight for remedial actions. In strategy execution, performance management supports the development, implementation, and execution of projects that enhance an organization’s performance and strategy (Jackson, 2020). The focus should be on the bigger picture by examining the project’s effect on the organization’s long-term performance. Strategy execution is considered successful if it positively contributes to the organizations long-term performance.
Conclusion
In summary, the enterprise transformation process framework developed by Agile Dynamics offers logical and pragmatic rationale for effective strategy execution . Most organizations fail to execute strategies effectively due to a lack of capacity and disregard to the factors which undermine strategy execution. The model provides the capability to detect and address the multifaceted issues undermining the effective execution of strategies.
Therefore, through the enterprise transformation model, organizations develop their ability to execute strategies effectively. Strategy execution can be considered a system or process, and in both cases, it involves various stakeholders and steps.
Formulating a strategy is easy, but executing it is complex due to internal and external environmental factors. Organizations can control the internal environment, but the external factors are unexpected and out of control. Organizations must invest in adjustment mechanisms to cope with challenges posed by the external environment.
References
Barrows E. (2019). What is strategy execution? American Management Association.
Cheng, S. (2015). Translating strategy into implementation via capability-based planning. Master thesis; Business Information Technology.
Cognizant. 2014). Creating competitive advantage with strategic execution capability.
Delloitte. (2017). Executing your company’s growth strategy: Getting it right. Southeast Asia CFO Survey.
Fedato, G. A. L., Pires, V. M., & Trez, G. (2015). The future of research in strategy implementation in the BRICS context. Brazilian Business Review.
Gartner. (2021). How to excel at strategy and execution: An IT perspective.
Jackson, T. (2020). Project Performance Management: Maximize Project Returns. Learning Hub. https://learn.g2.com/project-performance-management
Kotnour, T. (2011). An Emerging Theory of Enterprise Transformations. Journal of Enterprise Transformation, 1(1), 48-70 https://doi.org/10.1080/19488289.2010.550669
Radomska, J. (2014). Model of success full strategy execution: Revising the concept. Problems of Management in the 21st century, 9(3).
Robinson, J. (2019). Capabilities-driven strategy: The key to getting your growth strategy right.
Scott, J. (2016). A Strategy execution process. Accelare. https://www.accelare.com/blog/a-strategy-execution-process
Srivastava A., Sushil. (2011). Adapt: The pillar of strategy execution process linking back to strategy.
Sull, D., Homkes, R., & Sull, C. (2015). Why strategy execution unravels—and what to do about it. Harvard Business Review. https://hbr.org/2015/03/why-strategy-execution-unravelsand-what-to-do-about-it
Wasserman, T. & Czarnecki, J. R. (2014). A framework for aligning strategy and execution. Paper presented at PMI Global
Congress 2014—North America, Phoenix, AZ. Newtown Square, PA: Project Management Institute.
Author